- Vital Shift
- Posts
- Creatine: The Smartest Bet In The Supplement Aisle?
Creatine: The Smartest Bet In The Supplement Aisle?
Issue #22 · Read Time: 5.5 minutes
Simplifying Health, Amplifying Longevity, One Shift at a Time

Creatine’s image is stuck in shaker bottles and locker rooms, so it’s still treated like an extra—a notion past its expiry date. Effort is a currency, and creatine improves the exchange rate enough to tilt results over months and years. This is the boring edge that snowballs, which is why creatine belongs on the essentials shelf, not the bonus pile.
What Needs to Shift?
In medical school, I treated supplements like contraband. Powder? Pill? Either glossy placebos or a fast lane to side effects. Supplements felt like crutches for people trying to rent discipline instead of grow it.
My classmates rolled their eyes at my stance.
At a medical school party, with booze-loosened tongues, the weightlifters bawled at me over the music.
“Still dodging creatine?” Another laughed, “Idiot! No wonder your bench press is stuck at 165-lbs.”
These weren’t supplement-shilling gym ‘bros’. They were future physicians capable of deadlifting 450 lbs and parsing forest plots on research papers. And they couldn’t believe that someone steeped in evidence-based medicine would shrug off the supplement with the fattest stack of trials behind it.
Truth? I hadn’t read a single paper. I made a judgment on vibes and bias and dressed it up as prudence. I wouldn't have bothered to reconsider if the knife-edge minds I trusted hadn't all stacked up on the same side, leaving me the foolish outlier.
A week with the literature and I ate crow.
Creatine has been vetted in 500+ studies over decades, and the evidence for its safety and real-world results has outlived a few prescription drugs.
Years later, after returning to the research repeatedly—more out of paranoia than curiosity—I still haven't found a reason to stop using it. If anything, the evidence has only become more lopsided.
More Than A Synthetic Lab Creation
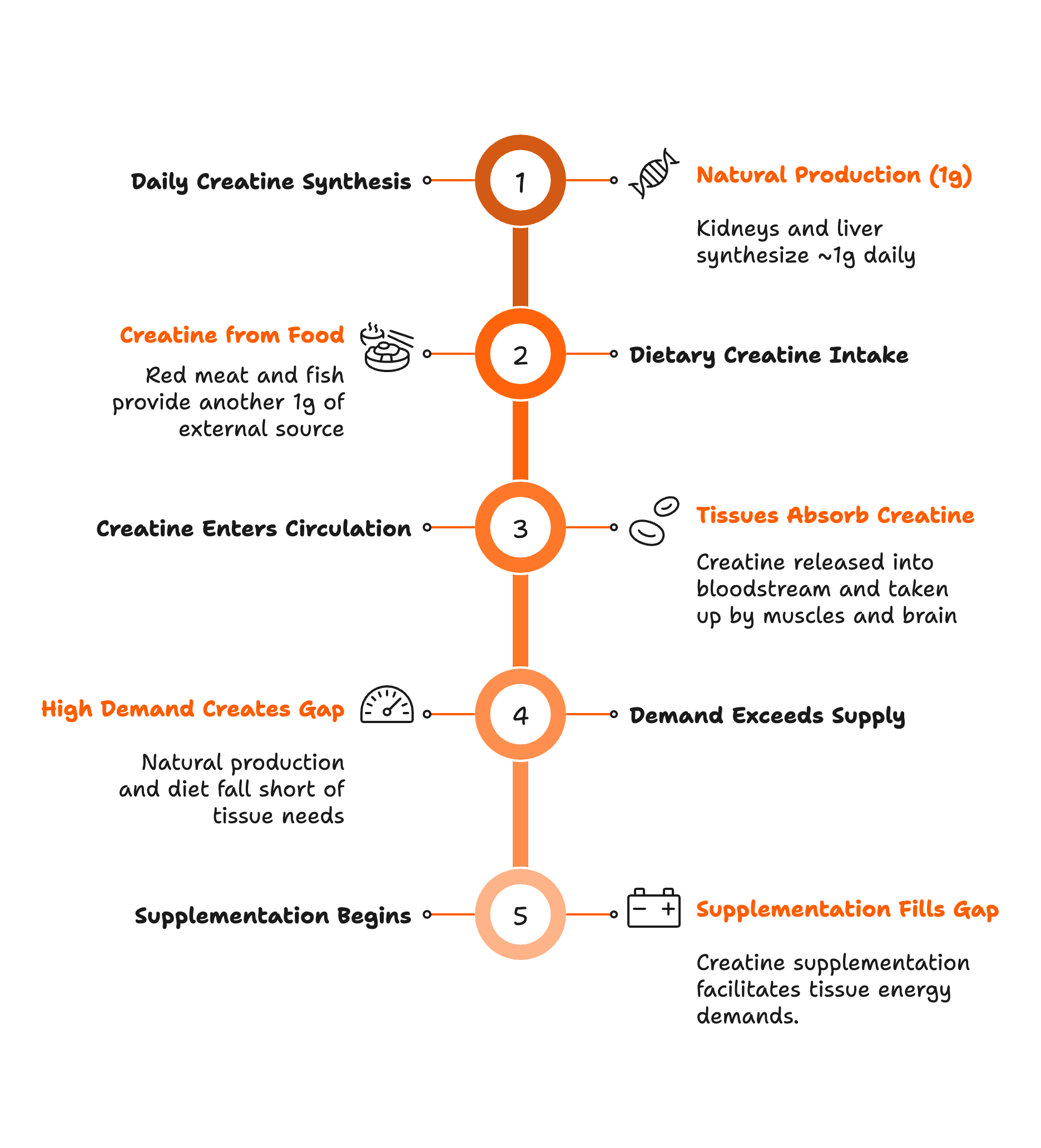
Creatinine isn’t some lab-only concoction. Your body naturally creates about 1-2g of creatine daily in the kidneys and liver.† ^
Once synthesized, or taken in through food (mostly red meat and fish)— about ~1g of external source— creatine slips into the bloodstream and gets hoarded by the body’s most power-hungry tissues: † ‡
🍖 Skeletal Muscle (the vault for ~95% of the body's creatine).
🧠 Brain (tucks away the remaining ~5%).
The problem? Even if you eat meat and fish, your body’s natural production and dietary intake dwarfs what your muscles and brain chew through, especially when operating at full throttle.
How Creatine Buys You Seconds
Your muscles and brain run on ATP (adenosine triphosphate)—the basic unit of cellular energy.
🔴 Constraint: Your cells only store enough ATP (energy) for a few seconds of maximum effort. After that, they have to pause and recharge to mint more ATP. That lag is what you feel as fatigue at the end of a lift or a sprint. Subsequently, you fail the rep or slow down.
🟡 Fix: Think of creatine like a portable charger. When ATP dies out under all-out effort, and the tank runs dry, you're forced to wait for the slow recharge cycle. Creatine molecules swoop in like backup battery packs, carrying a spare charge and transferring it to your dead battery instantly.† ‡
🟢 Upshot: You recharge the used-up ATP faster and buy yourself a few extra seconds of runway. Instead of hitting the wall at rep 8, you fail at rep 10. Instead of needing 3 minutes of rest, you recover in ~2 minutes.

More Work, More Muscle
If you read this newsletter then you know what we’re playing for.
Muscle mass, strength, and power are the most potent levers for healthspan and lifespan; grip strength, metabolic health, resistance to frailty, falls, odds of death—they all trace back to muscle. Therefore, anything that measurably grows it deserves a seat at your table.
⇥ Muscle growth follows a fundamental law: Total Load = Sets × Reps × Weight.
⇥ Creatine doesn’t flip a switch and hand you new strength. It delays the fatigue, letting you squeeze in more sets and reps before your tank runs empty.†
If creatine lets you squeeze 2 extra reps per set...
Across 5 exercises...
That’s an extra 30–50 reps per training session…
Over a year, that’s thousands of extra reps, compounding into more strength and muscle.

⇥ A meta-analysis of 22 studies show that training alone improved 1‑rep max by ~12%. Add creatine, and strength rose ~20%, an ~8% extra gain.†
⇥ For muscular endurance (repetitions to failure), the placebo training group improved by 12%, while the training group taking creatine improved by 26%, a 14% net gain.†
Cut to the studies that matter most in Appendix A.
Everyone Gains. These Two Gain The Most.
Two groups face specific biological gaps where creatine supplementation offers even greater leverage.
🥬 The Plant-Based Eater: Vegetarians and vegans get almost no creatine from food, leaving their muscle stores largely deficient. Supplementation often produces standout improvements in strength, lean mass, sprint performance, and cognitive measures.†
👵🏽 The Aging Adult: After 40, muscle loss (sarcopenia) speeds up, nudging the body toward weaker legs, slower reflexes, and a higher chance of falls and glucose dysregulation. One meta-analysis found that pairing creatine with resistance training added about 1.4 kg (~3 lb) more lean mass than training alone†. At 60, that extra muscle can be the difference between carrying your own suitcase and needing a hand, between steady steps and a stumble.‡
Your Next Move
The supplement aisle is a carnival of posturing circus clowns. You’ll see "advanced absorption," "liquid serums," and proprietary blends that charge you $50 for $5 worth of ingredients. Cut through the neon.
💹 The Cost of Entry
Only two seals matter:
Creapure® Seal: This isn't a brand. In short, it's proof of origin. It guarantees the creatine was manufactured with the highest purity standards with nothing else hitchhiking along.
NSF Certified for Sport Seal: This is a finished product test that guarantees that your exact batch has been tested for banned substances. Think of it as a safety promise.
Some marquee brands skip the Creapure licensing fee, betting that their in-house testing and NSF certification are the sturdier proof. Flip the tub and look for either of the two seals. You don’t need both.
Cost: For 500 g, expect ~$30–50 CAD ($25–35 USD). NSF often costs more, but I’m happy to pay for the purity.
My Choice: Thorne Creatine (not sponsored).
💤 Buy Boring
Creatine comes in a few different formulations. Start with creatine monohydrate. It’s the most studied, most effective, and easiest on your wallet.‡
Trap: Skip "Hydrochloride," "Ethyl Ester," or liquid forms. They are more expensive and the studies don’t show any measurable edge.‡
Exception: A tiny sliver of people get bloating or cramps from monohydrate.
Fix: Only if monohydrate bothers your stomach, switch to creatine hydrochloride. It’s gentler on your gut, but you’ll pay double.
🥣 Staying Afloat
Creatine tastes like nothing and feels gritty, like fine sand on your tongue. Try these tricks to make it go down easy:
Toss a scoop into your protein shake or smoothie.
Stir it into hot tea, or warm water for better dissolution.
Mix it in a small glass of water, swirl it into a whirlpool, and knock it back before the powder sinks.
Don’t fuss about timing. Pre-workout, post-workout, or with breakfast; just get it down the hatch.
💊 Dial In Your Daily Dose
The "5 grams for everyone" rule is a blunt heuristic. It suits a 150‑pound runner, but under-doses a 220 lb lifter. You don't fill a go‑kart and a truck with the same amount of fuel.
Research sets the minimum dose at ~0.03 g per kg‡. But we’re not here to scrape the bottom. For a 120-lb (55 kg) person, that works out to ~2 grams. Round up!
For most active adults (140–180 lbs), 3-5 g is the bulls eye.‡
If you weigh more than 200 lbs (90 kg) or carry a lot of muscle, aim for 8–10 g per day.‡
Do the math, then round up generously (aiming closer to ~5g for most). Up to 30g has been proven safe in clinical trials.‡
🔄 Skip The Loading Phase
The old guard says to "load up" with 20 grams a day for the first week, then reduce to your maintenance dose you calculated above.
The problem is that it can trigger bloating, which makes some people prematurely quit before they see results.
Unless you’re desperate to fast-track it, start with your daily maintenance dose each day. Your muscles will top in about 3–4 weeks. No need to “load up”.
Here’s what the next 12 weeks will feel like (so the scale doesn’t spook you):
Phase | What You Feel | What is Happening |
|---|---|---|
✅ Week 1 ↳ Getting Started | No performance change or noticeable effects yet. | Saturation Begins. Muscle creatine stores rise from ~120 to ~160 mmol/kg. Your tank is filling up. |
💧Week 2-4 ↳ Water Weight | Scale goes up 2–4 lbs (1-2 kg). Clothes fight slightly more snug around shoulders, chest and legs. | Cellular Hydration. This is not fat. It is increased water drawn inside the muscle cell, resulting in “weight gain”. It won’t widen your waist and isn’t a reason for concern. |
📈 Month 1 ↳ Performance Improves | Able to perform extra reps at a given weight. Slightly shorter rest between sets. Faster recovery. “I didn’t fail at rep 8”. | Increased Stimulus. Your muscles refill their working energy faster between efforts, so you tire later and can squeeze in more reps. |
🏋🏽♀️ Month 3+ ↳ Gains Compound | Small but noticeable strength and muscle size improvements. | Muscle Growth. Those extra reps each session add up. More total work over time builds strength and muscle. |
Your Shift In Review
Creatine isn’t synthetic. Your body already makes it, and your muscles and brain are built to use far more than diet alone can supply.
It works by refilling your energy stores faster, letting you push harder, recover quicker, and delay fatigue during exercise.
More total load = ↑ muscle = ↑ strength, metabolism, and longevity.
Muscle is the currency of longevity: protection against frailty, metabolic decline, falls, and early death.
Creatine only works if you do the work (i.e. lifting, sprinting). It doesn’t benefit couch potatoes.
Plant-based eaters and adults over 40 stand to gain the most because they start with the least margin.
Creatine nudges your training in small, repeatable ways. A couple more reps. A bit more iron moved. Let those small bumps stack like coins in a jar, and the pile starts to matter. Eventually, creatine stops feeling like a “supplement” and starts feeling like brushing your teeth; something you don’t debate, you just do.
One Last Pulse Check
📁Missed an issue? The archive is where the threads connect.
🔍 Next Issue: you got the “what” today. Next issue is the “why it works” breakdown, the parts people hand-wave because they only half understand them.
🏋🏽 Once a month I share my training logbook, what I’m testing, what I’m never doing again and the lessons that keep haunting me. Read last month’s sweat equity post.
📤 If you enjoyed this read, the best compliment I could receive would be if you shared it with one person who thinks creatine is just for gym rats.
I'm a Toronto doctor caring for older adults in hospitals and nursing homes, while spending my spare time digging into longevity science. I'm here to share what I'm learning. No fancy jargon, just practical insights to help you read your body’s early signals. Think of me as your friendly guide, figuring this out alongside you. Medicine has changed, but how we practice it hasn't caught up. That's why I'm here: to help you edit your health story while the early drafts are still open.
Appendix A
Study & Design | Key Outcomes | So What? |
The Performance Benchmark ↦ Rawson & Volek (2003) ↦ Meta-Analysis of 22 Studies | Hundreds of athletes. Compared to placebo, creatine users saw: +8% greater increase in Max Strength (1 rep max). +14% greater increase in weightlifting performance (endurance at max reps). | The "Tax" of Not Taking It. This study established the baseline "opportunity cost." If you train without creatine, you are voluntarily accepting a 14% deficit in work capacity. |
The "Real Muscle" Proof ↦ Volek et al. (1999) ↦ Randomized Controlled Trial, n=19 (Biopsy Study) | Participants performed heavy weightlifting for 12 week. Muscle biopsies revealed: Type I (Endurance) Fibers: +35% size (vs +11% placebo). Type II (Fast-Twitch) Fibers: +36% size (vs +15% placebo). Squat Strength: +32% (vs +24%). | Muscle Growth, Fiber by Fiber. This small but invasive study was crucial because it showed that the the gains were structural protein, not just fluid. |
The "Satellite Cell" Discovery ↦ Randomized Controlled Trial, n=32 (16 weeks) | Satellite Cell Count: Creatine users showed significantly higher proliferation of satellite cells (muscle stem cells) at weeks 4 and 8 compared to protein or placebo. These cells donated new nuclei to the muscle fibers, allowing for long-term growth potential. | The "Not Just Water" Smoking Gun. Stem Cell Activation. This is the rebuttal to the "it's just water weight" myth. Water weight doesn't create stem cells. This study demonstrates that creatine creates a cellular environment that actively recruits the body's repair machinery. |
The Frailty Defense ↦ Chilibeck et al. (2017) ↦ Meta-Analysis, n=721 (age 57–70) | Aggregated data from older adults performing weight training. Lean Tissue: Creatine groups gained 1.37 kg (3 lbs) more muscle than placebo groups. Strength: Significant improvements in chest press and leg press independent of training volume. | Independence Insurance. In a 57-year-old, 3 lbs of functional tissue is often the physiological difference between living at home and moving into assisted care. |
The Body Composition Standard ↦ Branch (2003) ↦ Meta-Analysis of 100 Studies | Reviewed outcome measures across diverse populations. Short-term: Average gain of 0.5–1.0 kg (mostly hydration). Training: Average gain of 1.0–2.5 kg greater lean mass than placebo over 4–12 weeks. | The "1-2kg" Reality. This massive data set normalizes the "weight gain" fear. It confirms that the scale will go up, but in individuals who train, a significant portion of that is muscle mass. |
The Recovery Signal ↦ Cooke et al. (2009) ↦ n=14 (Eccentric Damage Protocol) | Subjects performed a workout to batter their muscles. Creatine users showed: Lower CK levels: (Creatine Kinase, a marker of muscle damage) was 84% lower at 48 hours post-workout. Preserved Strength: Strength recovered 10% faster than placebo. | The "Bounce Back." Shows that creatine doesn’t clock out when the workout ends; it’s for the days after. It reduces the cellular wreckage of hard training, allowing for higher frequency and consistency. |
Reply